Which two types of granular RBAC does Nutanix provide for AHV hosts? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AD
Nutanix provides two types of granular RBAC for AHV hosts: category based and cluster based3. Category based RBAC allows administrators to assign roles to users or groups based on categories, which are key-value pairs that can be applied to various entities in Prism Central, such as clusters, hosts, VMs, images, and networks. Categories can be used to group entities by different criteria, such as department, project, environment, or location. For example, an administrator can create a category key named Department and assign different values to it, such as Finance, Marketing, or Engineering. Then, the administrator can apply this category to different clusters or hosts and assign roles to users or groups based on this category. This way, users or groups can have different levels of access to different clusters or hosts depending on their department4. Cluster based RBAC allows administrators to assign roles to users or groups based on specific clusters registered in Prism Central. For example, an administrator can create a role named Cluster Admin and assign it to a user or group for a particular cluster. This way, the user or group can have full access to that cluster and its hosts and VMs, but not to other clusters5.
Reference: Role-Based Access Control
https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Nutanix-Security-Guide-v6_7:sec-cluster-rbac-pc-c.html
An administrator wants to have a VM on an AHV cluster with access to multiple VLANs. What is the most efficient way to achieve this?
Correct Answer:
A
According to the Nutanix Support & Insights web search result2, VM NICs on AHV can operate in two modes: Access and Trunked. Access NICs are the default, and allow one VLAN on the NIC. Trunked NICs allow multiple VLANs on a single NIC for VMs that are VLAN aware. If you must use trunked NICs, follow the steps described in the web search result2. Therefore, the most efficient way to have a VM on an AHV cluster with access to multiple VLANs is to update a vNIC on the VM to operate in trunked mode for all desired VLANs.
Refer to the exhibit.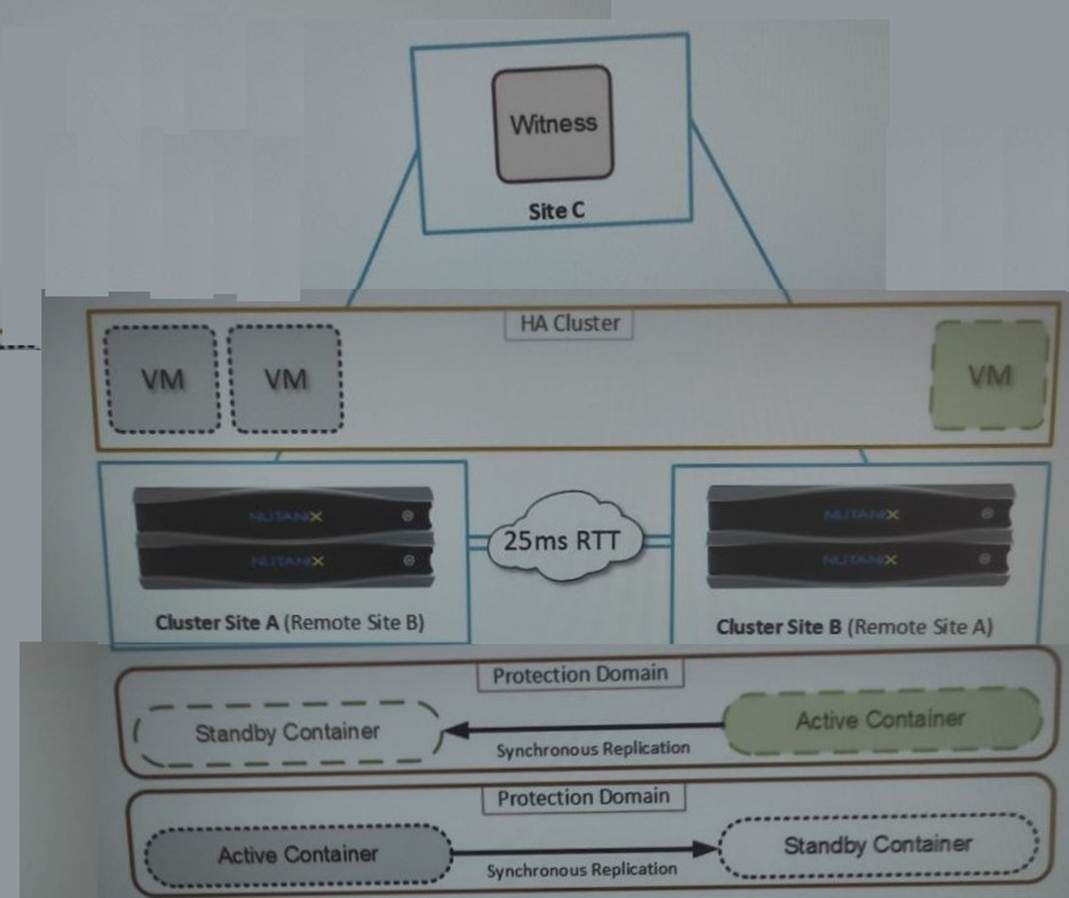
An administrator is trying to implement the solution that is shown in the exhibit, but has been unsuccessful.
Based on the diagram, what is causing the issue?
Correct Answer:
C
The correct answer is C. Network latency.
The diagram shows a solution that uses synchronous replication between two remote protection domains, cluster site A and cluster site B. Synchronous replication is a feature that allows near-zero RPO (recovery point objective) by replicating data to the remote site before acknowledging writes to the local site. However, synchronous replication has some requirements and limitations that must be met for it to work properly. One of these requirements is that the network latency between the two sites must be less than or equal to 5 ms1. If the network latency is higher than 5 ms, the synchronous replication will fail and the protection policy will be suspended2.
Therefore, based on the diagram, the most likely cause of the issue is that the network latency between cluster site A and cluster site B is higher than 5 ms, which prevents the synchronous replication from working. To verify this, the administrator can use the ??ncli cluster ping?? command to measure the network latency between the two sites3. If the network latency is indeed higher than 5 ms, the administrator can either improve the network performance or switch to a different replication mode, such as near-synchronous or asynchronous.
Reference: Synchronous Replication Requirements
Which inefficient VM Profile can be used to identify a VM that consumes too many resources and causes other VMs to starve?
Correct Answer:
C
A bully VM is a VM that consumes too many resources and causes other VMs to starve. A bully VM can affect the performance and availability of other VMs on the same host or cluster by hogging CPU, memory, disk, or network resources. A bully VM can be identified by using the VM Profile feature in Prism Central2. The VM Profile feature analyzes the resource utilization of each VM and assigns it a profile based on its efficiency and impact on other VMs. The profiles are as follows3:
✑ Efficient: The VM is well-provisioned and has optimal resource utilization.
✑ Over-provisioned: The VM has more resources than it needs and has low resource utilization.
✑ Constrained: The VM has less resources than it needs and has high resource utilization.
✑ Inactive: The VM has no resource utilization and is idle or powered off.
✑ Bully: The VM has high resource utilization and causes contention for other VMs. To identify a bully VM, the administrator can use Prism Central to view the VM Profile dashboard and filter by profile type. The dashboard shows the number of VMs in each profile type, as well as their resource consumption and efficiency score. The administrator can also drill down into each VM to see its detailed metrics and recommendations for optimization.
Reference: VM Profile
An administrator needs to configure a new subnet on an AHV cluster and want to ensure that VMs will automatically be assigned an IP address at creation time.
Which type of network does the administrator need to create?
Correct Answer:
C
A managed network is a type of network that can be created on an AHV cluster and allows VMs to automatically be assigned an IP address at creation time. A managed network uses the Nutanix IP Address Management (IPAM) service, which provides DHCP and DNS functionality for the VMs on the network. A managed network can be configured with a subnet range, a default gateway, and DNS servers. The IPAM service will allocate IP addresses from the subnet range to the VMs and register their hostnames in the DNS servers. The IPAM service will also release the IP addresses when the VMs are deleted or moved to another network1.
To create a managed network on an AHV cluster, the administrator can use Prism Element or Prism Central. The steps are as follows2:
✑ In Prism Element, go to the Network Configuration page and click Create Network.
✑ In Prism Central, go to the Networks page and click Create.
✑ Enter a name and description for the network.
✑ Select Managed as the network type.
✑ Enter the subnet range, default gateway, and DNS servers for the network.
✑ Optionally, enable VLAN tagging and enter a VLAN ID for the network.
✑ Click Save.
Reference: Nutanix AHV Networking Best Practices

