An analyst is building a search to examine Windows XML Event Logs, but the initial search is not returning any extracted fields. Based on the above image, what is themost likelycause?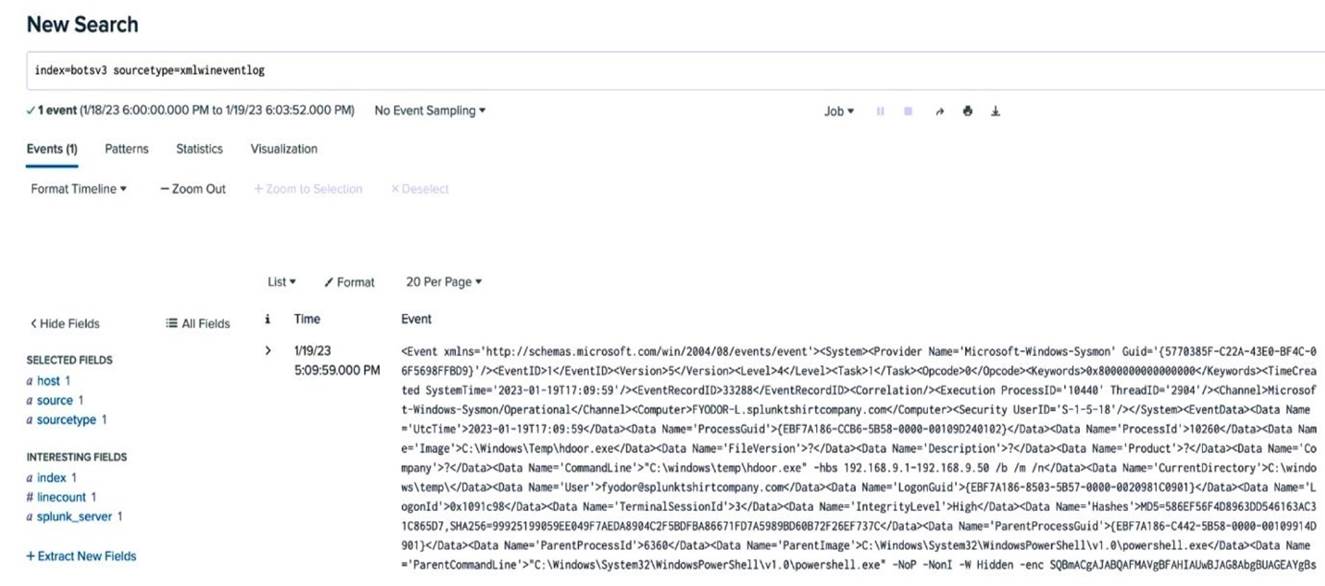
Correct Answer:
D
In Splunk, when an analyst is building a search and finds that extracted fields are not appearing, it often relates to the search mode being used.Smart ModeorVerbose Modeare better suitedfor field extraction as they allow Splunk to automatically extract and display fields based on the data being searched.
✑ Search Modes in Splunk:
✑ Incorrect Options:
✑ Splunk Documentation:Search modes and their impact on field extraction.
The United States Department of Defense (DoD) requires all government contractors to provide adequate security safeguards referenced in National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-171. All DoD contractors must continually reassess, monitor, and track compliance to be able to do business with the US government.
Which feature of Splunk Enterprise Security provides an analyst context for the correlation search mapping to the specific NIST guidelines?
Correct Answer:
D
Splunk Enterprise Security provides a feature calledFramework Mappingthat allows correlation searches to be mapped to specific cybersecurity frameworks, including NIST 800-171, which is crucial for DoD contractors. This mapping provides context to the analyst by showing how particular searches align with compliance requirements, aiding in continuous monitoring and reassessment as mandated by the DoD. This feature is integral for organizations that need to demonstrate compliance with NIST guidelines and other security frameworks.
An analyst is investigating how an attacker successfully performs a brute-force attack to gain a foothold into an organizations systems. In the course of the investigation the analyst determines that the reason no alerts were generated is because the detection searches were configured to run against Windows data only and excluding any Linux data.
This is an example of what?
Correct Answer:
C
This scenario is an example of aFalse Negativebecause the detection mechanisms failed to generate alerts for a brute-force attack due to a misconfiguration—specifically, the exclusion of Linux data from the detection searches. A False Negative occurs when a security control fails to detect an actual malicious activity that it is supposed to catch, leading to undetected attacks and potential breaches.
The following list contains examples of Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs):
* 1. Exploiting a remote service
* 2. Lateral movement
* 3. Use EternalBlue to exploit a remote SMB server In which order are they listed below?
Correct Answer:
A
The examples provided correspond to Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) in the following order:
✑ Lateral movement– This is aTactic. Tactics represent the goals or objectives of an adversary, such as moving laterally within a network to gain broader access.
✑ Exploiting a remote service– This is aTechnique. Techniques are specific methods used to achieve a tactic, such as exploiting a service to move laterally.
✑ Use EternalBlue to exploit a remote SMB server– This is aProcedure. Procedures are the detailed steps or specific implementations of a technique, such as using the EternalBlue exploit to target SMB vulnerabilities.
Thus, the correct order isTactic, Technique, Procedure.
The Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain® breaks an attack lifecycle into several stages. A threat actor modified the registry on a compromised Windows system to ensure that their malware would automatically run at boot time. Into which phase of the Kill Chain would this fall?
Correct Answer:
D
The Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain® is a widely recognized framework that breaks down the stages of a cyber attack. The stages are: Reconnaissance, Weaponization, Delivery, Exploitation, Installation, Command and Control (C2), and Actions on Objectives. The scenario described—modifying the registry on a compromised Windows system to ensure malware runs at boot time—fits into theInstallationphase. This phase involves placing a persistent backdoor or other malicious software on the victim's system, ensuring it can be executed again, even after a system reboot. By modifying the registry, the attacker is achieving persistence, a classic example of the Installation phase.

