- (Topic 2)
Which of the following cables replaced the Apple 30-pin connector and is also reversible?
Correct Answer:
B
Lightning Connector: Apple introduced this brand-new connector back in 2012. It is over 80% smaller than the 30-pin connector and is reversible. https://www.cablewholesale.com/support/technical_articles/whats_your_port.php#:~:text=Li ghtning Connector: Apple introduced this,pin connector and is reversible.
- (Topic 3)
A technician needs to configure a printer for network communications Which of the following must the technician configure? (Select THREE).
Correct Answer:
CDG
To configure a printer for network communications, the technician must configure its network settings, such as gateway, subnet mask, and IP address. The gateway is the IP address of the router or device that connects the printer to other networks or the internet. The subnet mask is a value that defines which part of the IP address identifies the network and which part identifies the host or device on that network. The IP address is a unique identifier that allows the printer to communicate with other devices.
- (Topic 4)
Multiple users contact the help desk to report issues with the network fileshares. Files are accessible, but performance is very slow. Which of the following should a technician perform first?
Correct Answer:
C
The correct answer is C. Check the RAID drive status LEDs.
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, which is a technology that combines multiple physical disks into a logical unit that provides improved performance, reliability, or both1. RAID can be implemented using hardware or software, and there are different levels of RAID that use different methods of data distribution and redundancy1. One of the common issues with RAID is disk failure, which means that one or more of the disks in the array stop working properly. Disk failure can affect the performance and availability of the network fileshares, depending on the RAID level and the number of failed disks2. For example, RAID 0, which uses striping to split data across multiple disks, has no redundancy and will lose all data if any disk fails. RAID 1, which uses mirroring to duplicate data on two disks, can tolerate one disk failure and still function. RAID 5, which uses striping with parity to distribute data and error correction information across three or more disks, can also tolerate one disk failure and still function1.
One of the ways to detect disk failure is to check the RAID drive status LEDs, which are lights that indicate the health and activity of each disk in the array. Different RAID controllers may have different LED patterns and colors, but generally, a green LED means that the disk is working normally, a red LED means that the disk has failed or is offline, an amber LED means that the disk is degraded or rebuilding, and a blinking LED means that the disk is active or busy34.
The first step that a technician should perform when troubleshooting network fileshare issues is to check the RAID drive status LEDs to see if any disk has failed or is degraded. This can help identify the cause of the problem and determine the appropriate solution. For example, if a disk has failed in a RAID 1 or RAID 5 array, the technician can replace the failed disk and rebuild the array to restore performance and redundancy. If a disk has failed in a RAID 0 array, the technician will need to restore the data from a backup2.
The other options are not the best steps to perform first. Defragmenting the files on the network share may improve performance by reducing fragmentation, but it will not solve the problem if there is a disk failure in the RAID array. Asking the users to perform a network speed test may help diagnose network issues, but it will not help identify disk issues in the RAID array. Starting the process of rebuilding the array may be necessary after replacing a failed disk, but it should not be done before checking the RAID drive status LEDs.
- (Topic 2)
A user reports limited or no connectivity on a laptop. A technician runs ipconf ig /all with the following result: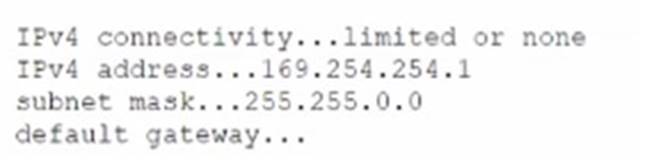
Which of the following is the MOST likely cause of this issue?
Correct Answer:
A
- (Topic 2)
A technician responds to a help desk ticket that indicates a user's workstation is not booting. The technician initially suspects a failed hard drive. The technician performs diagnostics and confirms the hard drive is fully operational.
Which of the following steps should the technician complete NEXT?
Correct Answer:
D
Since the hard drive appears to be functioning normally, the technician should investigate other potential causes of the issue. This could include checking the BIOS settings, verifying the connections to the hard drive, and testing the RAM. Once these steps have been completed, the technician can then take the necessary steps to resolve the issue.

